भारतातील मूळ भाषिकांच्या संख्येनुसार भाषांची यादी
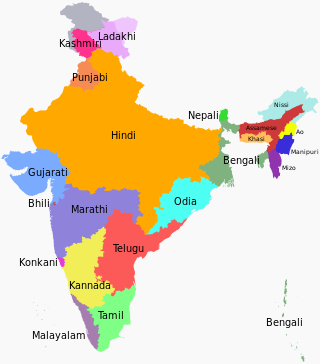
भारत वेगवेगळ्या शंभर भाषांचे घर आहे. बहुतेक भारतीय हिंद-आर्य समूहील (७४%) भाषा बोलतात जी इंडो-युरोपियन भाषांची ही एक शाखा आहे. द्रविड (२४%), ऑस्ट्रोएस्ट्रीएटिक (मुंडा) (१.२%) आणि साइनो-तिबेटी (०.६%) सुद्धा बोलली जाते. या व्यतिरिक्त हिमालयाची काही भाषा आज ही वर्गीकृत नाही. एस आई एल एथनोलॉगच्या सूची नुसार भारतात ४१५ जीवंत भाषा आहेत.
आढावा
संपादनIndia has 23 constitutionally recognized official languages. Hindi and English are the official languages used by the Central Government. State governments use respective official languages.
Hindi is the most widely spoken language in northern parts of India. The Indian census takes the widest possible definition of "Hindi" as a broad variety of "Hindi languages". According to 2001 Census, 53.6% of Indian population declared that they speak Hindi either as first or second language, in which 41% of them have declared it as their native language or mother tongue. 13% Indians declared that they can speak English as a second language.
Thirteen languages account for more than 1% of Indian population each, and between themselves for over 95%; all of them are "scheduled languages of the constitution". Scheduled languages spoken by fewer than 1% of Indians are Santali (0.63%), Kashmiri (0.54%), Nepali (0.28%), Sindhi (0.25%), Konkani (0.24%), Dogri (0.22%), Meitei (0.14%), Bodo (0.13%) and Sanskrit (In the 2001 census of India, only 14,135 people reported Sanskrit as their native language). The largest language that is not "scheduled" is Bhili (0.95%), followed by Gondi (0.27%), Khandeshi (0.21%), Tulu (0.17%) and Kurukh (0.10%).
Indian population in 1991 exhibited 19.4% of bilingualism and 7.2% of trilingualism, so that the total percentage of "native languages" is at about 127%.
India has a Greenberg's diversity index of 0.914, i.e. two people selected at random from the country will have different native languages in 91.4% of cases.
मूळ भाषिकांच्या संख्येनुसार भाषांची यादी
संपादनOrdered by number of speakers as first language.
More than one million speakers
संपादनThe 2001 census recorded 29 individual languages as having more than 1 million native speakers (0.1% of total population). The languages in bold are scheduled languages (the only scheduled language with less than 1 million native speakers is Sanskrit). The first table is restricted to only speaking populations for scheduled languages.
| Language | First language speakers[२][३] |
First language speakers as a percentage of total population[४] |
Second language speakers[३] |
Third language speakers[३] |
Total speakers[३][५] | Total speakers as a
percentage of total population[४] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hindi[b] | 422,048,642 | 41.03 | 98,207,180 | 31,160,696 | 551,416,518 | 53.60 |
| Bengali | 83,369,769 | 8.10 | 6,637,222 | 1,108,088 | 91,115,079 | 8.86 |
| Telugu | 74,002,856 | 7.19 | 9,723,626 | 1,266,019 | 84,992,501 | 8.26 |
| Marathi | 71,936,894 | 6.99 | 9,546,414 | 2,701,498 | 84,184,806 | 8.18 |
| तमिळ | 60,793,814 | 5.91 | 4,992,253 | 956,335 | 66,742,402 | 6.49 |
| Urdu | 51,536,111 | 5.01 | 6,535,489 | 1,007,912 | 59,079,512 | 5.74 |
| Kannada | 37,924,011 | 3.69 | 11,455,287 | 1,396,428 | 50,775,726 | 4.94 |
| Gujarati | 46,091,617 | 4.48 | 3,476,355 | 703,989 | 50,271,961 | 4.89 |
| Odia | 33,017,446 | 3.21 | 3,272,151 | 319,525 | 36,609,122 | 3.56 |
| Malayalam | 33,066,392 | 3.21 | 499,188 | 195,885 | 33,761,465 | 3.28 |
| English | 226,449 | 0.02 | 86,125,221 | 38,993,066 | 125,344,736 | 12.18 |
| Sanskrit | 14,135 | <0.01 | 1,234,931 | 3,742,223 | 4,991,289 | 0.49 |
| Rank | Language | 2001 census[६] (total population 1,028,610,328 ) |
1991 census[७] (total population 838,583,988) |
Encarta 2007 estimate[८] (worldwide speakers)
| ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | Speakers | Percentage | Speakers | ||
| 1 | Hindi[९] | 422,048,642 | 41.1% | 329,518,087 | 39.29% | 366 M |
| 2 | Bengali | 83,369,769 | 8.11% | 69,595,738 | 8.30% | 207 M |
| 3 | Telugu | 74,002,856 | 7.19% | 66,017,615 | 7.87% | 69.7 M |
| 4 | Marathi | 71,936,894 | 6.99% | 62,481,681 | 7.45% | 68.0 M |
| 5 | तमिळ | 60,793,814 | 5.91% | 53,006,368 | 6.32% | 66.0 M |
| 6 | Urdu | 51,536,111 | 5.01% | 43,406,932 | 5.18% | 60.3 M |
| 7 | Gujarati | 46,091,617 | 4.48% | 40,673,814 | 4.85% | 46.1 M |
| 8 | Kannada | 37,924,011 | 3.69% | 32,753,676 | 3.91% | 35.3 M |
| 9 | Malayalam | 33,066,392 | 3.21% | 30,377,176 | 3.62% | 35.7 M |
| 10 | Odia | 33,017,446 | 3.21% | 28,061,313 | 3.35% | 32.3 M |
| 11 | Punjabi | 29,102,477 | 2.83% | 23,378,744 | 2.79% | 57.1 M |
| 12 | Assamese | 13,168,484 | 1.28% | 13,079,696 | 1.56% | 15.4 M |
| 13 | Maithili | 12,179,122 | 1.18% | 7,766,921 | 0.926% | 24.2 M |
| 14 | Bhili/Bhilodi | 9,582,957 | 0.93% | |||
| 15 | Santali | 6,469,600 | 0.63% | 5,216,325 | 0.622% | |
| 16 | Kashmiri | 5,527,698 | 0.54% | |||
| 17 | Nepali | 2,871,749 | 0.28% | 2,076,645 | 0.248% | 16.1 M |
| 18 | Gondi | 2,713,790 | 0.26% | |||
| 19 | Sindhi | 2,535,485 | 0.25% | 2,122,848 | 0.253% | 19.7 M |
| 20 | Konkani | 2,489,015 | 0.24% | 1,760,607 | 0.210% | |
| 21 | Dogri | 2,282,589 | 0.22% | |||
| 22 | Khandeshi | 2,075,258 | 0.21% | |||
| 23 | Kurukh | 1,751,489 | 0.17% | |||
| 24 | Tulu | 1,722,768 | 0.17% | |||
| 25 | Meitei (Manipuri) | 1,466,705* | 0.14% | 1,270,216 | 0.151% | |
| 26 | Bodo | 1,350,478 | 0.13% | 1,221,881 | 0.146% | |
| 27 | Khasi | 1,128,575 | 0.11% | |||
| 28 | Mundari | 1,061,352 | 0.103% | |||
| 29 | Ho | 1,042,724 | 0.101% | |||
* Excludes figures of Paomata, Mao-Maram and Purul sub-divisions of Senapati district of Manipur for 2001.
** The percentage of speakers of each language for 2001 has been worked out on the total population of India excluding the population of Mao-Maram, Paomata and Purul subdivisions of Senapati district of Manipur due to cancellation of census results.
100,000 to one million speakers
संपादन| Rank | Language | 2001 census | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | ||
| 30 | Kui | 916,222 | 0.089% |
| 31 | Garo | 889,479 | 0.086% |
| 32 | Tripuri | 854,023 | 0.083% |
| 33 | Lushai/Mizo | 674,756 | 0.066% |
| 34 | Halabi | 593,443 | 0.058% |
| 35 | Korku | 574,481 | 0.056% |
| 36 | Miri/Mishing | 551,224 | 0.054% |
| 37 | Munda | 469,357 | 0.046% |
| 38 | Karbi/Mikir | 419,534 | 0.041% |
| 39 | Koya | 362,070 | 0.035% |
| 40 | Ao | 261,387 | 0.025% |
| 41 | Savara | 252,519 | 0.025% |
| 42 | Konyak | 248,109 | 0.024% |
| 43 | Kharia | 239,608 | 0.023% |
| 44 | English | 226,449 | 0.022% |
| 45 | Malto | 224,926 | 0.022% |
| 46 | Nissi/Dafla | 211,485 | 0.021% |
| 47 | Adi | 198,462 | 0.019% |
| 48 | Thado | 190,595 | 0.019% |
| 49 | Lotha | 170,001 | 0.017% |
| 50 | Coorgi/Kodagu | 166,187 | 0.016% |
| 51 | Rabha | 164,770 | 0.016% |
| 52 | Tangkhul | 142,035 | 0.014% |
| 53 | Kisan | 141,088 | 0.014% |
| 54 | Angami | 132,225 | 0.013% |
| 55 | Phom | 122,508 | 0.012% |
| 56 | Kolami | 121,855 | 0.012% |
| 57 | Khond/Kondh[१०] | 118,597 | 0.012% |
| 58 | Dimasa | 111,961 | 0.011% |
| 59 | Ladakhi | 104,618 | 0.010% |
| 60 | Sema | 103,529 | 0.010% |
भाषिकांच्या संख्येनुसार मातृभाषांची यादी
संपादनEach of the languages of the 2001 census subsumes one or more mother tongues. Speaker numbers are available for these mother tongues and they are also included in the speaker numbers for their respective language. The following table lists those mother tongues that have more than one million speakers. Per the General Notes from the 2001 census: "Mother tongue is the language spoken in childhood by the person’s mother to the person. If the mother died in infancy, the language mainly spoken in the person’s home in childhood will be the mother tongue."[११]
| Rank | Mother tongue | 2001 census | Included in language | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Speakers | Percentage | |||
| 1 | Hindi | 257,919,635 | 25.071% | |
| 2 | Bengali | 82,462,437 | 8.016% | |
| 3 | Telugu | 73,817,148 | 7.176% | |
| 4 | Marathi | 71,701,478 | 6.970% | |
| 5 | तमिळ | 60,655,813 | 5.896% | |
| 6 | Urdu | 51,533,954 | 5.009% | |
| 7 | Gujarati | 45,715,654 | 4.444% | |
| 8 | Kannada | 37,742,232 | 3.669% | |
| 9 | Bhojpuri | 33,099,497 | 3.217% | Hindi |
| 10 | Malayalam | 33,015,420 | 3.209% | |
| 11 | Odia | 32,110,482 | 3.121% | |
| 12 | Punjabi | 28,152,794 | 2.737% | |
| 13 | Rajasthani | 18,355,613 | 1.784% | Hindi |
| 14 | Magadhi/Magahi | 13,978,565 | 1.359% | Hindi |
| 15 | Chhattisgarhi | 13,260,186 | 1.289% | Hindi |
| 16 | Assamese | 12,778,735 | 1.242% | |
| 17 | Maithili | 12,178,673 | 1.184% | |
| 18 | Haryanvi | 7,997,192 | 0.777% | Hindi |
| 19 | Marwari | 7,936,183 | 0.771% | Hindi |
| 20 | Santali | 5,943,679 | 0.578% | |
| 21 | Malvi | 5,565,167 | 0.541% | Hindi |
| 22 | Kashmiri | 5,362,349 | 0.521% | |
| 23 | Mewari | 5,091,697 | 0.495% | Hindi |
| 24 | Khortha/Khotta | 4,725,927 | 0.459% | Hindi |
| 25 | Bhili/Bhilodi | 3,313,481 | 0.322% | |
| 26 | Bundeli/Bundelkhan | 3,072,147 | 0.299% | Hindi |
| 27 | Nepali | 2,867,922 | 0.279% | |
| 28 | Bagheli | 2,865,011 | 0.278% | Hindi |
| 29 | Pahari | 2,832,825 | 0.275% | Hindi |
| 30 | Lamani/Lambadi | 2,707,562 | 0.263% | Hindi |
| 31 | Awadhi | 2,529,308 | 0.246% | Hindi |
| 32 | Wagdi | 2,510,811 | 0.244% | Bhili |
| 33 | Gondi | 2,505,247 | 0.244% | |
| 34 | Harauti | 2,462,867 | 0.239% | Hindi |
| 35 | Konkani | 2,420,140 | 0.235% | |
| 36 | Dogri | 2,282,547 | 0.222% | |
| 37 | Garhwali | 2,267,314 | 0.220% | Hindi |
| 38 | Nimadi | 2,148,146 | 0.209% | Hindi |
| 39 | Sadan/Sadri | 2,044,776 | 0.199% | Hindi |
| 40 | Kumaoni | 2,003,783 | 0.195% | Hindi |
| 41 | Dhundhari | 1,871,130 | 0.182% | Hindi |
| 42 | Ahirani | 1,865,813 | 0.181% | Khandeshi |
| 43 | Kurukh/Oraon | 1,737,044 | 0.169% | |
| 44 | Tulu | 1,720,422 | 0.167% | |
| 45 | Sindhi | 1,694,061 | 0.165% | |
| 46 | Meitei | 1,466,497 | 0.143% | |
| 47 | Surgujia | 1,458,533 | 0.142% | Hindi |
| 48 | Bagri Rajasthani | 1,434,123 | 0.139% | Hindi |
| 49 | Bodo/Boro | 1,330,775 | 0.129% | |
| 50 | Banjari | 1,259,821 | 0.122% | Hindi |
| 51 | Nagpuria | 1,242,586 | 0.121% | Hindi |
| 52 | Surjapuri | 1,217,019 | 0.118% | Hindi |
| 53 | Kangri | 1,122,843 | 0.109% | Hindi |
| 54 | Mundari | 1,046,951 | 0.102% | |
| 55 | Ho | 1,037,987 | 0.101% | |
संदर्भ
संपादन- ^ "Report of the Commissioner for linguistic minorities: 50th report (July 2012 to June 2013)" (PDF). Commissioner for Linguistic Minorities, Ministry of Minority Affairs, Government of India. 17 September 2016 रोजी पाहिले.
- ^ ORGI. "Census of India: Comparative speaker's strength of Scheduled Languages-1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001".
- ^ a b c d S, Rukmini. "Sanskrit and English: there's no competition".
- ^ a b http://www.censusindia.gov.in/Census_Data_2001/India_at_glance/popu1.aspx
- ^ "Indiaspeak: English is our 2nd language - Times of India".
- ^ a b Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues – 2000, Census of India, 2001
- ^ Comparative Speaker's Strength of Scheduled Languages -1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001, Census of India, 1991
- ^ "Languages Spoken by More Than 10 Million People – Table – MSN Encarta". 2007-12-03 रोजी मूळ पान पासून संग्रहित. Unknown parameter
|deadurl=ignored (सहाय्य) - ^ includes Western Hindi apart from Urdu, Eastern Hindi, Bihari languages except for Maithili, the Rajasthani languages, and the Pahari languages apart from Nepali and (in 2001) Dogri, whether or not the included varieties were reported as "Hindi" or under their individual names.
- ^ different from Kui language
- ^ Census Data 2001 General Notes
चुका उधृत करा: "lower-alpha" नावाच्या गटाकरिता <ref>खूणपताका उपलब्ध आहेत, पण संबंधीत <references group="lower-alpha"/> खूण मिळाली नाही.
